- Position: MECE Programme > Programme Details >
- Programme Details
Program Duration:2 years
Degree Awarded: Master of engineering in electronics and communication engineering (MECE)
Curriculum:
Curriculum:
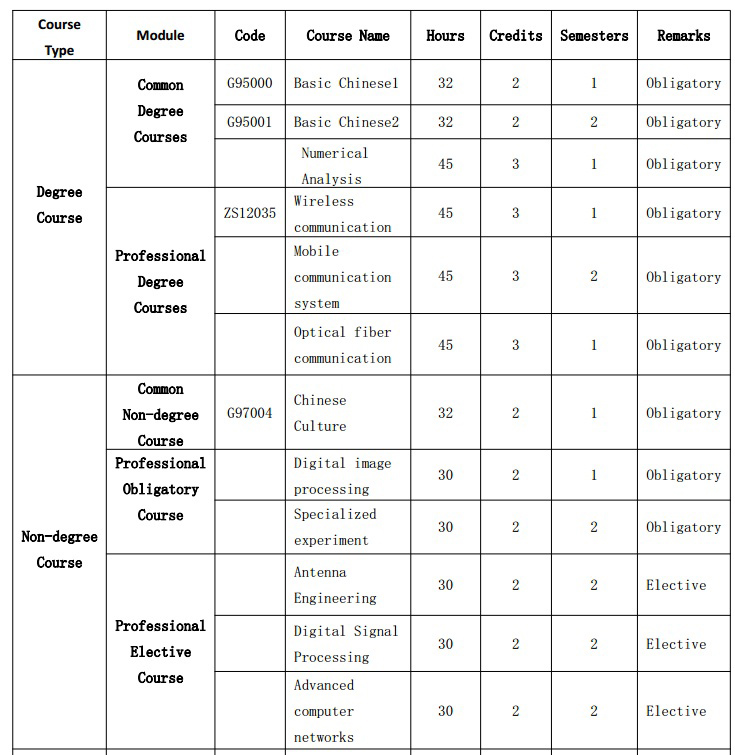
Course Description:
1.Wireless communication
Wireless communications is the communication specialty course. This course will cover advanced topics in wireless communications for voice, data, and multimedia. We begin with a brief overview of current wireless systems and standards. We then characterize the wireless channel and examine the Capacity of Wireless Channels. Our next focus will be on digital modulation techniques, adaptive modulation and diversity techniques, MIMO and space-time coding, multicarrier modulation, spread Spectrum, and equalization etc. The course is very important to train the students to grasp and know the wireless communication techniques and richen their specialty knowledge background, develop their engineering skills for their future jobs and work experiences.
Text book: Andrea Goldsmith(USA), Wireless communications, Posts & Telecommunications Press, Beijing, 2007.12
Originally published by Cambridge University Press in 2005.
2.Mobile communication system
Mobile wireless communication has become an important part of modern life, from global cellular telephone systems to local and even personal-area networks. This course provides a main introduction to digital mobile wireless networks, illustrating principles, characteristics,development and applications of mobile communication. This course begins with a review of propagation phenomena, and goes on to examine channel allocation, modulation techniques, multiple access schemes, and coding techniques. GSM, IS-95, 2.5G and 3G packet-switched systems are discussed in detail. Wireless LANs and personal-area networks are introduced simply, and 4G is also given a description. The course closes with an introduction to new key techniques, such as Diversity, Equalization, Interleave, Rake, MUD, Power Control, DBF, OFDM, MIMO etc.
Text book: Mischa Schwartz(USA), Mobile wireless communications, Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, 2005.7
Originally published by Cambridge University Press in 2005.
3.Digital image processing
Digital image processing is closely related to everyday life and high end technology, from making a picture look better to image compression and object recognition, all subject are with practical importance. This course stresses the basic principle, algorithm design and program of image processing. The course begins with image enhancement in spatial and frequency domain, emphasize various techniques such as gray-level transformation, histogram processing, mask convolution etc. and their subjectivity, then goes further to discuss image restoration methods and their objectivity, including three basic restoration methods: observation, experimentation, and mathematical modeling, emphasize discussion on denoising and estimating degradation function.
Followed by a brief introduction on image compression and wavelet concept, its transformation and application in image compression. Then briefly discuss image dilation and erosion. The course ends with image segmentation and representation concept. Commonly used image transformation methods are discussed along the way, specifically they are 2-D Fourier transform, DCT transform, Hough transform, discrete K-L transform.
Text book: Rafael C. Gonzalez (USA), Digital Image Processing, Second edition, Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, 2002.7
4.Optical fiber communication
As one of the milestones of modern communication network, optical fiber communication has been deployed worldwide since 1980 and has indeed revolutionized the technology behind telecommunications. The objective of this course is to understand the optical fiber communication system in a comprehensive manner. The emphasis is on the fundamental aspects, but the engineering issues are also discussed. This course begins with the historical perspective on the development of optical communication system and basic concepts. Then the components of the optical fiber communication system are studied in detail, including the optical fibers, optical sources and optical receivers. This course finishes with the introduction of new technologies, such as EDFA, RA, soliton system, etc.
Text book: Fiber Optic Communications, By Joseph C. Palais, 5th Edition, Pearson Prentice Hall, 2005;
Optical Fiber Communications, By G. Keiser, 3rd Edition, MeGraw Hill, 2000
5. Antenna Engineering
Since Hertz and Marconi, antennas have become increasingly important to our society until now they are indispensable, especially to the rapidly developed modern wireless communications. The course addresses fundamental and advanced topics in antennas. The contents of the course include: introduction to antenna basics, electromagnetic radiation, antenna fundamentals, aperture antenna, microstrip antenna, array antennas and synthesis, self and mutual impedance and coupling, introduction to smart antennas system aspects, antenna measurement techniques, etc.
Text book:Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, By Constantine A. Balanis, 3rd edition, Wiley, 2005;
Antenna Theory and Design, By Warren L. Stutzman and Gary A. Thiele, 2nd edition, 1998.
6. Digital signal processing
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) is concerned with the representation, transformation and manipulation of signals on a computer. After half a century advances, DSP has become an important field, and has penetrated a wide range of application systems, such as consumer electronics, digital communications, medical imaging and so on. The course covers the concepts and techniques of modern digital signal processing which are fundamental to all the above applications. The objective of this course is to understand and implement theoretical concepts, methods and algorithms. The course starts with a detailed overview of discrete-time signals and systems, representation of the systems by means of differential equations, and their analysis using Fourier and z-transforms. The sampling theory of continuous-time signals is explained next, followed by exploring the transform-based analysis of linear time-invariant (LTI) systems and their structures. Subsequently, the notion of discrete Fourier transform is introduced, followed by an overview of fast algorithms for its computation. Then,principal methods for design of filters are covered. Finally, the applications of digital signal processing including speech processing and spectrum analysis are introduced.
Text book: Discrete Time Signal Processing, by A.V. Oppenheim and R.W. Schafer, Prentice Hall, Third Edition.2009
Applied Digital Signal Processing, by D. Manolakis and V. Ingle, Cambridge University Press, 2011
7. Advanced Computer Networks
This course covers advanced topics of computer networks. It is designed for graduate students at College of Communication Engineering, Chongqing University. This graduate-level course studies fundamental concepts, systems aspects and emerging technologies of computer networks. The goal of this course is to explore the key technical and research topics in computer networks as well as to convey the necessary analytical and evaluation techniques. This course consists of two parts. Part I studies the key concepts and protocols of computer networks. Main topics include: layered network architectures, physical layer, data link layer (PPP, CSMA/CD), medium access sub-layer (Ethernet, Wi-Fi), network layer (IP, RIP, OSPF, BGP), transport layer (TCP/UDP, congestion control), and application layer. Part II studies the advanced computer networking technologies. Main topics include: optical networks (optical switching, optical routing, FTTX broadband access networks, optical network control plane, etc), cloud data center networks (cloud, data center, storage networking, etc), and future Internet (OpenFlow, Software Defined Network, etc). Lectures are complemented with reading, homework, and research reports.
Text book: Computer Networks: A Systems Approach (5th edition), by Larry L. Peterson and Bruce S. Davie. Morgan Kaufmann. 2012
8. Experiments of DSP, FPGA , and Embedded System
DSP Experiment Course:
As one of the most important EDA tools, DSPs technology plays critical role in the fields of communication and signal processing. The content of the DSP experiment course consists of the follow:
(1) the primary architecture and features of the DSPs.
(2) the software and hardware developing environments.
(3) the system implementation procedure in the term of DSPs. Therefore, the major experiments include “CCS Software Tool”, “C & Assemble Instruction”, “McBSP Interface”, “FIR Filter” as well as “DSP BIOS”.
This course is suited for the undergraduate and graduate students. “Digital Circuit” and “Digital Signal Processing” are required as the previous fundament for this course.
FPGA Experiment Course:
FPGA technology is a useful EDA tool, which is applied widely in the development of digital electronic system. The purpose of this course is to enable students master the developing flow and do development independently with VHDL including Sequential Logic Circuits and Combinational Logic Circuit. Our study will focus on the following:
(1) Quartus II software tool
(2) Architecture and Feature of FPGA
(3) State Machines
(4) Application of LPM and MegaCore
(5) Analysis and Optimization.
Embedded System Experiment Course:
Embedded systems are omnipresent and play significant roles in modern-day life. Embedded systems are also diverse and can be found in consumer electronics,in industrial robots,in advanced avionics,in medical equipment, in automotive designs and in some other technical fields. This is an introductory course on embedded systems. This course begins with a review of embedded system hardware architecture and embedded processor and goes on to principles of real-time embedded operating system. Then the booting process of embedded system is discussed. Finally the development process of embedded system should be grasped by students.
Text book: Qing Li and Carolyn Yao. Real-Time Concepts for Embedded Systems,published by CMP Books. April 2003
